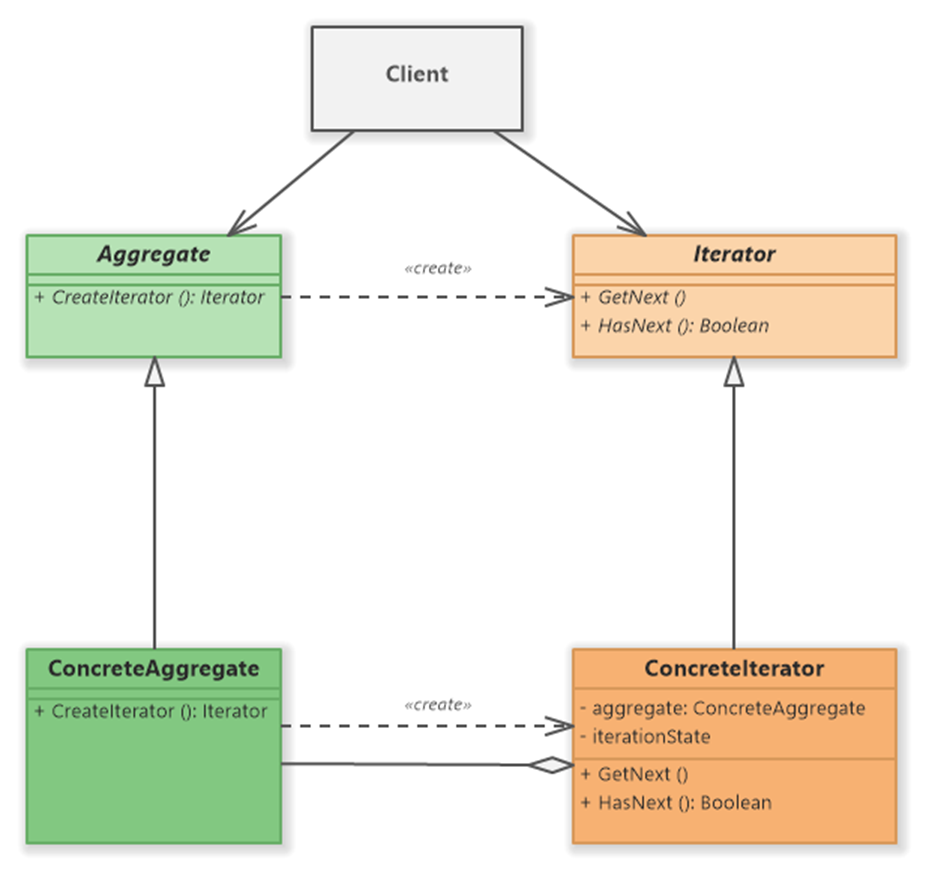
The Iterator design pattern is a behavioral design pattern that provides a way
to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation.
It allows clients to iterate over a collection of objects in a standardized manner,
abstracting away the details of the iteration process.
// Step 1: Iterator interface
interface Iterator<T> {
boolean hasNext();
T next();
}
// Step 2: Concrete Iterator
class ListIterator<T> implements
Iterator<T> {
private List<T> list;
private int index;
public ListIterator(List<T> list) {
this.list = list;
this.index = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < list.size();
}
@Override
public T next() {
return list.get(index++);
}
}
// Step 3: Aggregate interface
interface Aggregate<T> {
Iterator<T> createIterator();
}
// Step 4: Concrete Aggregate
class ListAggregate<T> implements
Aggregate<T> {
private List<T> list;
public ListAggregate() {
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void add(T element) {
list.add(element);
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> createIterator() {
return new ListIterator<>(list);
}
}
// Step 5: Client code
public class IteratorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListAggregate<String> aggregate
= new ListAggregate<>();
aggregate.add("A");
aggregate.add("B");
aggregate.add("C");
Iterator<String> iterator
= aggregate.createIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
class Book {
private String title;
public Book(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}
class BookIterator implements Iterator {
private BookCollection collection;
private int index;
public BookIterator(BookCollection collection) {
this.collection = collection;
this.index = 0;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < collection.size();
}
public Object next() {
return collection.get(index++);
}
}
class BookCollection extends ArrayList<Book> {
public Iterator<Book> getIterator() {
return new BookIterator(this);
}
@Override
public boolean add(Book e) {
super.add(e);
return true;
}
}
public class BookIteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookCollection collection = new BookCollection();
collection.add(new Book("The Java Book"));
collection.add(new Book("Design Patterns"));
Iterator<Book> iterator = collection.getIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Book book = iterator.next();
System.out.println(book.getTitle());
}
}
}